
Everything You Need To Know About 8 Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are labels we give to words based on the job they do in a sentence. Whether a word names something, describes something, or connects ideas, in the end, it all comes down to its part of speech. Once you get the hang of them, building clear, strong sentences gets way easier.
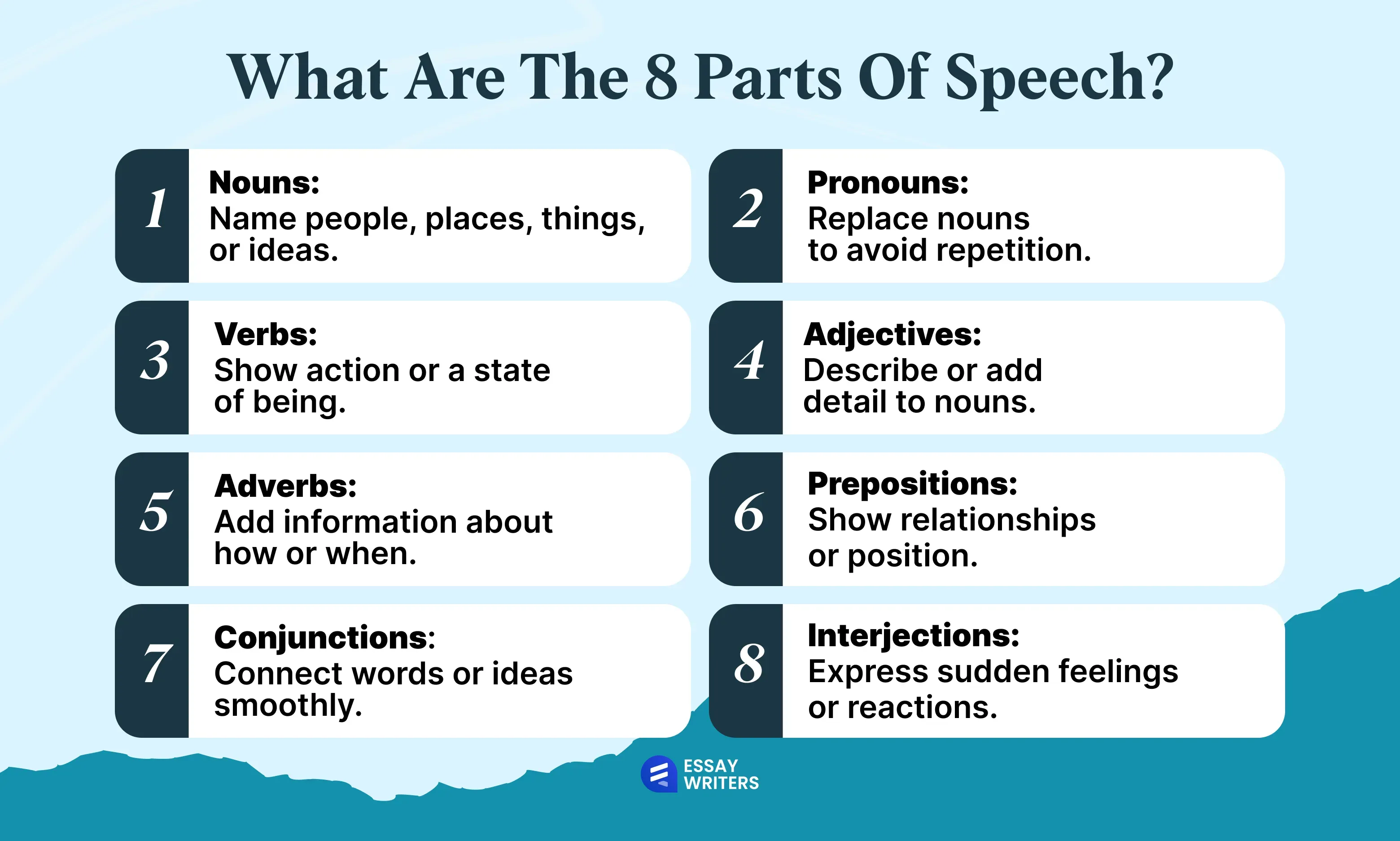
Let’s look closely at the list of different parts of speech placed in alphabetical order:
- Adjectives.
- Adverbs.
- Conjunctions.
- Interjections.
- Nouns.
- Prepositions.
- Pronouns.
- Verbs.
Read this article so you can easily identify 8 parts of speech and write grammatically correct sentences. By the way, if you don't have enough time to tweak every minor grammar error in your papers, EssayWriters' professional essay writers can always step in and give you expert writing help.
8 Parts of Speech in English
English relies on structure. That structure starts with knowing what each word is doing. The rest of the article will cover the different parts of speech in detail.
Nouns
A noun is basically the name of a person, place, thing, or idea. It answers simple questions like “Who?” or “What?”Think of things you can touch, like a bird or a table, or things you can’t see but still feel or understand, like love or time. Nouns are often the stars of the sentence (the subject), or they can be the things getting acted upon (the object).
- Actor, ice-cream, dog, love, patience.
Pronouns
Pronouns are like shortcuts in a sentence. They step in so you don’t have to repeat the same name or noun over and over. For example, instead of saying, “John went to John’s car because John was late,” you’d say, “John went to his car because he was late.” It instantly makes your writing flow better and sound less awkward.
- personal ( I, you, he, she, it, we, they, me, you, him, her, it, us, them).
- possessive (mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs, my, his, her).
- reflexive (myself, yourself, him-herself, itself).
- demonstrative (this, that, these, those).
- interrogative (who, whom, which, what).
Verbs
A verb indicates what's happening. It may explain something that someone is doing, something they are feeling, or even the mere existence of something. Verbs are what make sentences move forward. These elements indicate what the subject is doing, even if they're doing nothing more than being still or silently feeling something.
- swim, eat, take, have, seem, hear, listen, watch, see.
Regular verbs change in ways you can predict, while irregular ones don’t follow any clear pattern. With the former, you usually add -ed to form the past tense. Irregular verbs work differently: all you can really do is remember how they behave.
- I love reading comics → In my childhood, I loved reading comics.
- believe → believed
- train → trained
- wave → waved
- They eat vegetables on the farm. → Two weeks ago, they ate vegetables on the farm.
- come → came
- give → gave
- sing → sang
Adjectives
An adjective is a word that tells you more about a noun or pronoun, helping your reader picture exactly what you mean. Think about a car, for example. Is it a fast car? A rusty car? Without adjectives, your description stays vague. With them, you give clear details. Adjectives can go before the noun (a noisy classroom) or after the verb (The classroom is noisy), making your writing much more vivid.
- sad, big, tasty, loud, relaxed, red, thin.
- This happy little girl wore a bright red dress.
Adverbs
Adverbs are like sentence enhancers. They add extra detail by describing how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. They usually modify verbs, adjectives, or even other adverbs. Many end in -ly (like quickly or gently), but not all follow that rule (very, well, too are all adverbs too). Once you know what they do, they’re pretty easy to spot.
- Fast, there, never, rapidly, very, tomorrow.
- The meal was so delicious that he ate it quickly and passionately.
Prepositions
A preposition shows how one thing relates to another. You’ll usually find it sitting right before a noun, forming a little phrase that gives extra detail. It needs something after it to make sense, though. Phrases like on the table or during class are good examples of how prepositions work.
- in, on, under, near, after, before, during, between
The keys are inside the drawer.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions hold your ideas together. They are used to connect phrases or even whole ideas. If you are writing and want it to feel natural, you will need conjunctions to keep everything together.
There are three kinds:
Coordinating conjunctions join two complete ideas that feel equal, like in:
- I wanted to go for a walk, but it started raining.
Subordinating conjunctions introduce an additional idea to the main one:
- She stayed inside because the storm was getting worse.
And correlative conjunctions work in pairs:
- Not only did he clean the kitchen, but he also organized the fridge.
Interjections
An interjection is what someone blurts out when they react to something. It’s not part of the sentence in the usual way. You’ll often see it with an exclamation point, but not always. Words like wow, ugh, or hey don’t need to explain much. They show emotion in the moment, and that’s really all they’re there for. They don’t follow grammar rules, but they’re hard to miss.
- wow, ouch, hey, uh-oh, hmm, yay
Ouch! That coffee is hot.
(Ouch! expresses a sudden feeling.)
Identifying Different Parts of Speech
You can't always figure out which one of the eight parts of speech you're reading with one look. In cases like this, you must take a step back and figure out what the word is doing. The same word can have more than one job depending on its location.
- Check the word function. If it is referring to a person or thing, then it is probably a noun. If it is stating what is being done, it is likely a verb.
- Look at the surrounding words. A part of speech in front of a noun might be an adjective. A part of speech after a verb might be an adverb.
- Substitute it with another word of the same function. If it still makes sense, you probably got it right.
- Look at how the word conjugates. Is it changing tense to indicate past or present, or is it becoming plural? If so, you are probably dealing with a verb or a noun.
- Read the entire sentence aloud. Sometimes, hearing the flow of the sentence allows you to see how it functions.
Words That Switch Roles: Nouns, Verbs, and More
Some words are true shapeshifters. They don’t stick to just one role. Their function depends on where they appear in a sentence, which makes learning the parts of speech even more interesting.
Take play, for instance.
- They watched a play at the theater. (play is a noun).
- The kids play outside every afternoon. (play is a verb).
Or green:
- The green looks brighter after the rain. (green is a noun).
- She chose a green shirt for the party. (green is an adjective).
- They green the city by planting trees. (green is a verb).
This flexibility happens all the time, so you can’t always guess a word’s category. Look at the full sentence and ask what the word is doing. That question usually gives you your answer.
Final Thoughts
You don’t need to memorize every grammar rule, no one expects that. Honestly, it’s not even necessary. What is helpful, though, is getting a general feel for how the different parts of speech work. Once you start spotting the patterns, writing gets way easier. Everything just starts clicking into place.
If you're working through all of this and still not confident in grammar rules, EssayWriters' platform can come to the rescue with expert assistance. Our professional college essay writers assist students with all kinds of academic tasks, allowing them to sit back and take a breath.
FAQs
What Is a Part of Speech?
A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Every word you use, whether it’s naming something, describing an action, or linking ideas, falls into one of eight main parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, or interjection. Understanding these categories helps you build better sentences and make your writing clearer.
What Are the 8 Parts of Speech?
The 8 parts of speech are the basic building blocks of English grammar. They are: nouns (people, places, things), pronouns (replacements for nouns), verbs (actions or states), adjectives (describe nouns), adverbs (describe verbs/adjectives), prepositions (show relationships in space/time), conjunctions (connect words or phrases), and interjections (express emotion). Each plays a unique role in sentence structure.
Can a Word Belong to More Than One Part of Speech?
Yes, many words in English can belong to more than one part of speech, depending on how they’re used in a sentence. For example, “play” can be a verb (“They play soccer”) or a noun (“We watched a play”). The function of the word, what it’s doing in the sentence, determines its part of speech. That’s why understanding how a word works in a sentence helps identify its grammatical role accurately.
Sources
- Payne, L. (2023, October 20). Part of speech | Meaning, Examples, & English Grammar | Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/part-of-speech
- Butte College. (2019). The Eight Parts of Speech - TIP Sheets - Butte College. https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/grammar/parts_of_speech.html


